Generating leads is only half the battle in B2B marketing. The real challenge lies in knowing which leads actually matter.
Sales teams don’t fail because they lack leads, they fail because they spend time on the wrong ones. Marketing teams don’t struggle because they can’t drive traffic, they struggle because not all traffic converts into revenue. This is where lead scoring becomes one of the most important systems in modern B2B growth strategies.
Understanding what lead scoring is, how it fits into the broader lead qualification steps, and how to implement it correctly can dramatically improve conversion rates, shorten sales cycles, and align sales and marketing teams around a shared definition of success.
In this article, we’ll break down:
- What lead scoring really is in a B2B context
- Why it exists and what problems it solves
- How lead scoring fits into the full lead qualification process
- The different types of lead scoring models
- Common mistakes companies make
- And how to build a system that scales with your business
Whether you’re generating hundreds of leads a month or tens of thousands, lead scoring is what separates noise from opportunity.
What Is Lead Scoring?
Lead scoring is a systematic way of ranking and prioritizing leads based on how likely they are to become customers. Each lead is assigned a numerical score based on specific attributes and behaviors, allowing sales and marketing teams to focus their time and effort on prospects with the highest potential value rather than treating every lead equally.
In B2B environments, lead scoring is especially critical because:
- Sales cycles are longer, often spanning weeks or months and requiring sustained engagement
- Buying decisions involve multiple stakeholders, each with different priorities, levels of influence, and timelines
- Not every interested contact is ready to buy, even if they engage with content or respond to outreach
Without a scoring system in place, leads are often treated the same way, even though their intent, authority, and readiness can vary dramatically. This lack of differentiation leads to inefficient follow-up, missed opportunities, and unnecessary friction between sales and marketing teams.

Why Lead Scoring Matters in B2B Sales and Marketing
B2B marketing teams generate leads through many channels, content syndication, webinars, paid media, events, outbound campaigns, and more. But volume alone doesn’t drive revenue.
The Cost of Treating All Leads the Same
When every lead is sent directly to sales:
- Reps waste time chasing unqualified prospects
- Follow-up becomes inconsistent
- Conversion rates drop
- Sales loses confidence in marketing-generated leads
This creates friction between teams and slows growth.
Lead scoring acts as a filter, ensuring that sales teams focus their energy on leads that meet defined qualification criteria, while marketing continues to nurture those that aren’t ready yet.
Alignment Between Sales and Marketing
One of the biggest benefits of lead scoring is alignment. When both teams agree on:
- What a qualified lead looks like
- When a lead is ready for outreach
- How readiness is measured
The entire funnel becomes more efficient.
How Lead Scoring Fits Into Lead Qualification Steps
Lead scoring does not replace lead qualification, it supports it.
To fully understand how scoring works, it helps to look at the broader lead qualification steps in a typical B2B funnel.
Step 1: Lead Generation
This is where contacts first enter your ecosystem. Leads may come from:
- Downloading content
- Registering for webinars
- Filling out contact forms
- Engaging with ads
- Attending events
At this stage, interest exists, but intent is often unclear.
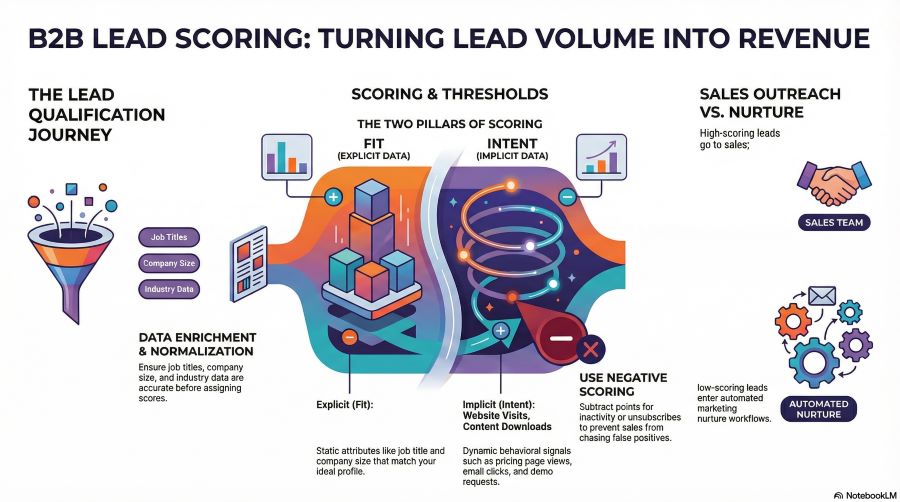
Step 2: Data Enrichment and Normalization
Before scoring can happen, lead data must be accurate and complete. This includes:
- Job title
- Company size
- Industry
- Location
- Email marketing validity
Incomplete or inaccurate data leads to misleading scores.
Step 3: Lead Scoring
This is where leads are evaluated based on:
- Who they are (fit)
- What they do (behavior)
Each action or attribute contributes to an overall score.
Step 4: Lead Qualification Thresholds
Once a lead reaches a certain score, it becomes:
- Marketing Qualified (MQL)
- Sales Accepted (SAL)
- Or Sales Qualified (SQL)
Scoring determines when leads move forward, and when they stay in nurture.
Step 5: Sales Outreach or Nurture
High-scoring leads go to sales. Lower-scoring leads remain in automated workflows until their behavior signals readiness.

The Two Core Components of B2B Lead Scoring
Effective lead scoring models are built on two main pillars: fit and intent.
Demographic and Firmographic Scoring (Fit)
This part of scoring evaluates whether a lead matches your ideal customer profile.
Common attributes include:
- Job title or role
- Department
- Seniority level
- Company size
- Industry
- Geographic location
For example:
- A Director at a mid-market SaaS company may score higher than an intern at a small agency
- A company within your target industry scores higher than one outside it
Behavioral Scoring (Intent)
Behavioral scoring evaluates what the lead is actually doing.
This may include:
- Website visits
- Content downloads
- Webinar attendance
- Email engagement
- Demo requests
- Pricing page views
The strongest leads score well in both categories.
Explicit vs Implicit Lead Scoring
Another way to understand what is lead scoring is to break it down into two core data types: explicit data and implicit data. Both play an important role in B2B lead scoring, but they serve different purposes and answer different questions.
Explicit Scoring
Explicit data is information the lead provides directly, either through forms, registrations, or profile details. This data helps establish who the lead is and whether they align with your ideal customer profile.
Explicit scoring commonly includes attributes such as:
- Job title, which helps determine role relevance and decision-making authority
- Company name, used to identify account fit and buying potential
- Industry, which indicates how closely the lead aligns with your target market
- Company size, often used to assess budget, complexity, and scalability
Because this information changes infrequently, explicit data is considered relatively static. It plays a critical role in defining fit, but on its own, it does not indicate when a lead is ready to engage in a sales conversation.
Implicit Scoring
Implicit data is based on observed behavior rather than self-reported information. It reflects how the lead interacts with your brand over time and provides insight into interest level and buying intent.
Implicit scoring is typically based on behaviors such as:
- Clicks on emails, ads, or calls to action
- Page views, particularly high-intent pages like pricing or product pages
- Time on site, which can signal depth of interest
- Content interactions, such as downloading assets or attending webinars
Unlike explicit data, implicit data is dynamic and constantly evolving. It captures momentum and urgency, making it especially valuable for timing sales outreach.
In B2B sales, implicit signals often matter more than explicit ones when determining when to act. A lead with a perfect job title but low engagement may need further nurturing, while a highly engaged lead with slightly less ideal fit may be ready for a timely conversation.

Common Lead Scoring Models Used in B2B
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to lead scoring, but several models are commonly used.
Points-Based Scoring
This is the most traditional model. Leads earn or lose points based on actions and attributes.
Example:
- +10 points for downloading a whitepaper
- +20 points for requesting a demo
- +15 points for a target job title
Once a lead crosses a predefined threshold, it’s considered qualified.
Threshold-Based Scoring
In this model, leads must meet specific criteria before being passed to sales.
For example:
- Company size over 200 employees
- Job title manager-level or higher
- At least two high-intent actions
This approach is stricter and reduces low-quality handoffs.
Predictive Lead Scoring
Predictive models use historical data and machine learning to identify patterns among past conversions. These models continuously adapt but require:
- Large data sets
- Clean CRM data
- Ongoing monitoring
While powerful, predictive scoring works best when layered on top of a strong foundational model.
Lead Scoring Mistakes That Hurt Conversion Rates
Many companies implement lead scoring but fail to see results because of common mistakes.
Over-Scoring Vanity Actions
Not all engagement signals equal buying intent. Actions like:
- Opening emails
- Visiting a blog post
- Clicking social links
May show interest, but not readiness.
Ignoring Negative Scoring
Lead scoring isn’t just about adding points. Subtracting points is just as important.
Examples include:
- Unsubscribes
- Long periods of inactivity
- Job titles outside target roles
Negative scoring helps prevent false positives.
Sending Leads to Sales Too Early
Premature handoffs frustrate sales teams and burn leads before they’re ready.
Lead scoring should protect sales time, not waste it.
How Lead Scoring Improves Sales Efficiency
When implemented correctly, lead scoring transforms how sales teams operate by removing guesswork and replacing it with clear, actionable signals. Instead of working from static lead lists or relying on intuition, sales reps can prioritize outreach based on real data.
Sales reps are able to:
- Spend more time on high-intent prospects, focusing their energy on leads that have demonstrated both fit and readiness
- Personalize outreach based on behavior, referencing specific pages viewed, content downloaded, or actions taken
- Shorten sales cycles by engaging leads at the right moment rather than too early or too late
- Increase close rates by prioritizing prospects who are already moving toward a buying decision
Instead of guessing who to call or email next, reps follow clear signals that indicate where their attention will have the greatest impact. This leads to better conversations, higher productivity, and less wasted effort across the sales team.

Lead Scoring and Long-Term Funnel Health
Lead scoring isn’t just a sales tool—it’s a funnel optimization tool that improves performance across the entire customer journey. By continuously evaluating lead behavior and fit, teams gain a clearer understanding of how prospects move through the funnel.
It allows marketing teams to:
- Segment audiences more effectively, grouping leads based on readiness, interest, and profile fit
- Personalize messaging so prospects receive content that aligns with their stage in the buying journey
- Nurture leads at the right pace, avoiding both over-communication and premature sales outreach
- Measure true funnel performance, using lead progression instead of raw volume as a success metric
Over time, this creates a more predictable and scalable revenue engine, one where leads are guided forward intentionally, sales and marketing stay aligned, and growth is driven by quality rather than guesswork.
Why Lead Scoring Is Essential for Sustainable B2B Growth
Understanding what lead scoring is means recognizing that it’s not about assigning random numbers or chasing vanity metrics, it’s about creating a shared language between marketing and sales. Lead scoring provides a consistent framework for evaluating leads, setting expectations, and determining when meaningful engagement should happen.
When combined with clearly defined lead qualification steps, lead scoring ensures that:
- Sales talks to the right people, focusing on prospects who match the ideal customer profile and show real buying intent
- Marketing focuses on quality, not just volume, optimizing campaigns around outcomes instead of raw lead counts
- Leads are nurtured instead of rushed, allowing trust and interest to develop naturally over time
- Growth becomes sustainable, driven by predictable processes rather than short-term tactics
In B2B environments where trust, timing, and relevance matter, lead scoring isn’t a shortcut or a quick fix, it’s a foundational system. When implemented thoughtfully and maintained over time, it supports stronger alignment, better customer experiences, and long-term revenue growth that scales with the business.
B2B Lead Scoring – FAQ’s
1. What is lead scoring in B2B?
Lead scoring is a method of ranking B2B leads based on fit and intent to determine sales readiness.
2. Why is lead scoring important?
It helps sales teams focus on high-quality leads and improves conversion rates.
3. What are the main lead qualification steps?
Lead generation, data enrichment, lead scoring, qualification thresholds, and sales or nurture handoff.
4. What data is used in lead scoring?
Firmographic data, demographic details, and behavioral engagement signals.
5. How do you know when a lead is sales-ready?
When it reaches a predefined score or meets qualification criteria agreed upon by sales and marketing.
6. Can lead scoring be automated?
Yes. Most marketing automation platforms support automated lead scoring models.
7. What’s the difference between MQL and SQL?
An MQL meets marketing criteria, while an SQL is ready for direct sales engagement.
8. How often should lead scoring models be updated?
Regularly—especially as buyer behavior, products, or markets change.
9. Does lead scoring replace sales judgment?
No. It supports sales decision-making but doesn’t eliminate human insight.
10. Is lead scoring useful for small B2B teams?
Yes. Even simple scoring models can significantly improve focus and efficiency.