
In today’s hyper-competitive digital marketplace, few channels deliver the consistent ROI and direct engagement that email marketing provides. In this Business Email List: A Comprehensive Guide, compiled by the marketing experts at Reach Marketing, you’ll explore every facet of email marketing success—from building responsive opt-in forms and crafting compelling lead magnets to mastering advanced segmentation, compliance, and automation. This guide is designed to empower businesses of all sizes to grow a robust, high-performing email list that drives conversions, builds lasting customer relationships, and remains legally compliant in an ever-evolving landscape.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- List Building
- 2.1 Opt-in Forms
- 2.2 Lead Magnets
- 2.3 Landing Pages
- 2.3.1 Subscriber Incentives
- 2.3.2 Content Upgrades
- Segmentation
- 3.1 Demographic Data
- 3.2 Behavioral Data
- 3.3 Psychographic Variables
- 3.3.1 Audience Personas
- 3.3.2 B2B vs B2C
- Compliance & Deliverability
- 4.1 CAN-SPAM
- 4.2 GDPR
- 4.3 IP Reputation
- 4.3.1 SPF & DKIM
- 4.3.2 Whitelisting
- Tools & Platforms
- 5.1 ESP (Email Service Provider)
- 5.2 CRM Integration
- 5.3 SMTP Services
- 5.3.1 Automation Workflows
- 5.3.2 Marketing Hub
- Personalization & Automation
- 6.1 Dynamic Content
- 6.2 Merge Tags
- 6.3 Triggered Emails
- 6.3.1 Behavioral Triggers
- 6.3.2 Drip Campaigns
- Maintenance & Hygiene
- 7.1 Bounce Management
- 7.2 Unsubscribe Handling
- 7.3 Email Validation
- 7.3.1 Re-engagement Campaigns
- 7.3.2 Suppression Lists
- Lead Generation & Conversion
- 8.1 Lead Scoring
- 8.2 Call-to-Action (CTA)
- 8.3 Funnel Optimization
- 8.3.1 Sales Enablement
- 8.3.2 Retargeting
- Analytics & Metrics
- 9.1 Open Rates
- 9.2 Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- 9.3 Conversion Rate
- 9.3.1 Return on Investment (ROI)
- 9.3.2 A/B Testing
- Data Security & Privacy
- 10.1 Encryption
- 10.2 Data Governance
- 10.3 Consent Management
- 10.3.1 Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
- 10.3.2 Privacy Policy
- Best Practices & Trends
- 11.1 Mobile Optimization
- 11.2 Plain Text vs HTML
- 11.3 AI-driven Campaigns
- 11.3.1 Interactive Emails
- 11.3.2 Dark Mode Adaptation
- FAQ
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
A Business Email List is more than just a collection of email addresses; it’s a direct conduit to potential customers, industry professionals, and key decision-makers. In an era where social media algorithms can unpredictably limit your reach, owning a high-quality, permission-based email list guarantees you a consistent channel to communicate your brand’s message.
- High ROI: According to multiple industry studies, every $1 spent on email marketing can generate up to $36 in return—a statistic often cited by marketing authorities like the DMA and ReachMarketing.com.
- Customer Engagement: Personalized emails see higher open rates and conversions, helping to build brand loyalty.
- Data Ownership: Unlike rented audiences on social networks, your email list is wholly yours, enabling greater control over how and when you engage subscribers.
In this extensive guide, we’ll explore how to build a robust email list, maintain its hygiene, comply with regulations, and leverage modern tools and best practices to stay ahead of the competition.

2. List Building
Business Email List Building typically starts with capturing the contact details of people who have expressed interest in your brand or offerings. A well-structured list-building strategy ensures higher engagement and lowers unsubscribes or spam complaints.
2.1 Opt-in Forms
An Opt-in Form is any form where potential subscribers actively provide their email address to receive further communication from you. This can appear on your:
- Homepage: Often above the fold or via a banner on the side.
- Blog Posts: Embedded within content or as a pop-up that activates after a certain period.
- Checkout Pages: Allowing customers to subscribe while making a purchase.
Key Components of Effective Opt-in Forms
- Compelling Headline: Clearly state what the subscriber gains.
- Minimal Fields: Typically, “Name” and “Email” are enough to reduce friction.
- Clear CTA: A button with text like “Join Now” or “Get My Free Guide.”
Best Practices
- Use Contrasting Colors: Make the form stand out from the page background.
- Placement Matters: High-traffic pages or relevant blog content can significantly boost opt-ins.
- Mobile-Responsiveness: Ensure the form is easy to fill out on small screens.
2.2 Lead Magnets
A Lead Magnet is an incentive offered to potential subscribers in exchange for their email address. Examples include:
- E-books or whitepapers
- Discount codes or free trials
- Webinar access or exclusive video content
According to ReachMarketing.com, well-targeted lead magnets can improve opt-in rates by up to 60%. The magnet should be:
- Immediate: Delivered as soon as the subscriber opts in.
- Relevant: Address a specific challenge or interest of your target audience.
- High-Value: Offer premium content, not just generic information.
2.3 Landing Pages
Landing Pages are standalone web pages designed with a single goal—converting visitors into leads or customers. When it comes to building email lists, these pages often focus solely on capturing email addresses.
- No Distractions: Remove navigation bars and external links.
- A/B Testing: Experiment with headlines, images, and CTAs to find the highest-converting layout.
- Trust Signals: Show testimonials or partner logos to establish credibility.
2.3.1 Subscriber Incentives
Subscriber Incentives are typically built right into your landing pages. Examples:
- Exclusive Pre-Launch Access
- VIP Event Invitations
- Personalized Consultation or Audit
These incentives work best when they’re tied directly to your core offer. For instance, a software company might offer a free 14-day trial, while a B2B consulting firm might offer a complimentary 30-minute strategy session.
2.3.2 Content Upgrades
A Content Upgrade is a specialized lead magnet offered within a specific piece of content. For instance, a blog post discussing “Top 10 B2B Marketing Tools” might include a downloadable PDF checklist that expands on each tool. This hyper-relevance increases the likelihood of readers opting in.
Table: Types of Content Upgrades
| Content Type | Upgrade Example | Value Provided |
|---|---|---|
| Blog Post (How-to Guide) | Step-by-Step PDF Checklist | Quick-reference material to apply the tutorial steps |
| Product Review | “Best Practices” Whitepaper | In-depth analysis and data supporting the product’s ROI |
| Webinar Archive | Companion Slide Deck Download | Additional references to complement the webinar topic |
| Data Report | Spreadsheet of Raw Data | Allows deeper personal analysis by the user |

3. Segmentation
Segmentation divides your email list into smaller, more targeted groups. Doing so ensures that content is relevant and resonates with each segment’s unique interests or needs, leading to higher open and click-through rates.
3.1 Demographic Data
Demographics often include age, gender, location, and profession (especially crucial for B2B). By knowing demographic data, you can tailor your messaging:
- Localized Offers: For region-specific promotions.
- Industry-Specific Language: Highlight solutions that match a particular sector’s pain points.
3.2 Behavioral Data
Behavioral Data involves how subscribers engage with your brand:
- Purchase History: Frequency, amount spent, product categories.
- Email Engagement: Open rates, click-throughs, and survey participation.
- Website Browsing: Pages visited, content downloads, or webinar attendance.
Marketers can use this data to build highly targeted automated campaigns. For example, a subscriber who repeatedly visits your “Pricing” page might receive a comparison chart or an invitation to a product demo.
3.3 Psychographic Variables
Psychographics delve into lifestyle, personality traits, attitudes, and values. Although more challenging to gather, psychographic segmentation can significantly boost personalization.
3.3.1 Audience Personas
Audience Personas are fictional representations of your ideal customers. They include:
- Background: Job title, industry, educational level.
- Goals: What they aim to achieve using your solution.
- Challenges: Pain points or obstacles they face.
Building personas helps you craft email content that resonates deeply with distinct audience groups.
3.3.2 B2B vs B2C
- B2B: Emphasize ROI, efficiency, and detailed data. Decision-making often involves multiple stakeholders.
- B2C: Lean toward emotional triggers, lifestyle imagery, and brand storytelling.
By understanding your audience’s context—whether B2B or B2C—you can segment effectively and deliver messages that align with their motivations.

4. Compliance & Deliverability
Without maintaining compliance and a positive sending reputation, even the best content can end up in spam folders. Deliverability hinges on both technical best practices and adherence to global regulations.
4.1 CAN-SPAM
In the United States, the CAN-SPAM Act dictates commercial email requirements:
- Accurate Headers & Subject Lines: No misleading information.
- Physical Address: Must be included in every commercial email.
- Easy Unsubscribe: One-click opt-out methods are recommended.
Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, so it’s crucial to align your practices with these guidelines.
4.2 GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) affects how companies handle the personal data of EU residents. Key principles:
- Lawful Basis for Processing: Typically consent or legitimate interest.
- Data Minimization: Collect only data necessary for your stated purpose.
- Right to Be Forgotten: Subscribers can request their data be deleted.
4.3 IP Reputation
Your IP Reputation is akin to a credit score for email sending. Consistent high-quality sends improve your standing with ISPs (Internet Service Providers), resulting in better inbox placement.
4.3.1 SPF & DKIM
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): Verifies the server sending the email is authorized by the domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Uses an encrypted signature in the email’s header to validate domain authenticity.
Both SPF and DKIM protect against email spoofing and help ISPs confirm that emails are legitimately from you.
4.3.2 Whitelisting
Encourage subscribers to add your sending address to their contact lists or mark your emails as “safe.” Whitelisting boosts delivery rates and signals ISPs that your messages are welcome.
5. Tools & Platforms
Choosing the right email marketing tools can streamline campaign creation, testing, and optimization. Below are some key categories of platforms.
5.1 ESP (Email Service Provider)
Popular ESPs include Mailchimp, Constant Contact, Klaviyo, and Campaign Monitor. Core features often include:
- Email Templates & Drag-and-Drop Builders
- List Segmentation & Management
- Basic Analytics (Opens, Clicks, Unsubscribes)
Tip: Look for an ESP that offers advanced segmentation, automation, and robust reporting if your business needs go beyond basic newsletter sending.
5.2 CRM Integration
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system like HubSpot, Salesforce, or Pipedrive stores comprehensive data on leads and customers:
- Unified Profiles: Centralize interactions across email, calls, and meetings.
- Sales Pipeline Visibility: Track the status of leads as they move toward conversion.
- Lead Scoring: Automate lead qualification based on behavior and demographic data.
Integration between your ESP and CRM ensures data flows seamlessly, enabling highly personalized email campaigns triggered by CRM updates.
5.3 SMTP Services
For high-volume senders or those needing more technical control, SMTP services like Amazon SES, SendGrid, or Mailgun offer:
- Scalable Sending Infrastructure
- Detailed API Endpoints
- Reputation Management Tools
These services are ideal for transactional emails, such as password resets or purchase confirmations, as well as marketing campaigns at scale.
5.3.1 Automation Workflows
Automation workflows allow you to set up a series of emails triggered by subscriber actions or attributes:
- Welcome Series: Introduce new subscribers to your brand and top products.
- Lead Nurturing: Gradually provide more in-depth information leading to a purchase.
- Re-engagement: Win back dormant subscribers who haven’t interacted in a while.
5.3.2 Marketing Hub
An all-in-one Marketing Hub (like HubSpot Marketing Hub or Marketo) consolidates:
- Email Marketing
- Social Media Management
- Lead Capture & Forms
- Advanced Analytics
These suites often include built-in CRM functionality, making them ideal for medium to large enterprises looking for a unified marketing ecosystem.

6. Personalization & Automation
Personalization and automation are the cornerstones of modern email marketing. By delivering content specific to each subscriber’s preferences or behaviors, you can drastically improve engagement metrics.
6.1 Dynamic Content
Dynamic Content shifts based on user attributes. For instance:
- Geographical Personalization: Display different offers based on the subscriber’s city or country.
- Purchase History Personalization: If the subscriber has purchased a certain product category, highlight complementary items.
This technique increases relevancy, thereby driving higher click-through rates and conversions.
6.2 Merge Tags
Merge Tags (also known as personalization tokens) insert subscriber-specific data into the email—most commonly the subscriber’s first name. For B2B, you could also include:
- Company Name: “Hello [Company], we have a new solution for you!”
- Job Title: “As a [Title], you know how important data security is.”
Such details create a connection that can significantly improve open and click rates.
6.3 Triggered Emails
Triggered Emails are initiated by specific actions or milestones in the subscriber’s lifecycle:
- Welcome Emails: Immediately after sign-up.
- Abandoned Cart Emails: E-commerce users who leave items in their cart.
- Milestone Emails: Birthday or membership anniversary messages.
6.3.1 Behavioral Triggers
Behavioral Triggers look for certain user actions, such as clicking on a promotional link. If someone repeatedly views a product demo page, your system might trigger a follow-up email offering a personalized demo session.
6.3.2 Drip Campaigns
A Drip Campaign is a scheduled set of emails sent over time, nurturing the subscriber from awareness to conversion. They can be based on time intervals (e.g., one email every five days) or triggered actions (e.g., email #2 only sends if email #1 was opened).

7. Maintenance & Hygiene
A high-performing Business Email List requires ongoing care. Maintenance and hygiene ensure you’re engaging genuine, interested recipients while preserving a strong sender reputation.
7.1 Bounce Management
- Soft Bounces: Temporary issues (e.g., mailbox full). Your system may attempt re-delivery.
- Hard Bounces: Permanent failure (e.g., invalid email address). These should be removed or flagged immediately.
Frequent hard bounces signal ISPs that your list may be outdated or purchased, which can harm deliverability.
7.2 Unsubscribe Handling
- Mandatory Opt-out Link: Required by laws like CAN-SPAM.
- One-click Process: Minimizes user frustration and negative impressions.
- Feedback or Preference Center: Optionally ask why they’re unsubscribing or offer reduced email frequency.
7.3 Email Validation
Email Validation Tools (e.g., ZeroBounce, NeverBounce) check for syntax errors, verify mail server existence, and identify role-based or disposable emails. Validating addresses before sending helps maintain a pristine reputation.
7.3.1 Re-engagement Campaigns
If a subscriber hasn’t opened or clicked on any emails for months, a re-engagement campaign can reignite interest:
- We Miss You: Offer a special discount or ask for updated preferences.
- Choose Your Own Content: Let them pick the frequency and type of emails they want to receive.
7.3.2 Suppression Lists
A Suppression List is a catalog of addresses you deliberately exclude from future sends. It might include:
- Unsubscribers
- Hard Bounces
- Complaints or Abuse Reports
By honoring these suppression lists, you maintain compliance and protect your IP reputation.
8. Lead Generation & Conversion
Email isn’t just for nurturing relationships—it’s a powerful channel for lead generation and driving conversions.
8.1 Lead Scoring
Lead Scoring assigns points to subscribers based on their interactions and profiles:
- Open & Click Behavior: Higher scores for more opens/clicks.
- Form Submissions: Downloads, demos requested, or webinar sign-ups.
- Demographic Fit: Industry, job title, or company size for B2B.
A high lead score signals sales-readiness, helping you focus on prospects most likely to convert.
8.2 Call-to-Action (CTA)
A CTA is the linchpin of any marketing email, telling subscribers exactly what next step to take. Effective CTAs:
- Use Action Verbs: “Download Now,” “Try Free,” or “Book a Demo.”
- Stand Out Visually: Contrasting colors and sufficient whitespace.
- Convey Immediate Value: “Unlock Your 20% Discount.”
8.3 Funnel Optimization
A well-optimized funnel guides leads from awareness to purchase with minimal friction. Email marketing plays a critical role at each stage:
- Top of Funnel (ToFu): Informative newsletters or blog highlights.
- Middle of Funnel (MoFu): Webinars, case studies, or product demos.
- Bottom of Funnel (BoFu): Personalized offers, free trials, or demos.
8.3.1 Sales Enablement
Sales Enablement aligns marketing efforts with sales objectives. By providing sales teams with relevant lead data and insights:
- Personalized Outreach: Sales reps can reference specific user actions or preferences in their communications.
- Consistency in Messaging: Ensure the same brand language and offer clarity across email campaigns and sales calls.
8.3.2 Retargeting
Retargeting extends your reach beyond the inbox by showing ads to users who engaged but didn’t convert. Sync your email list with platforms like Google Ads, LinkedIn, or Facebook Ads to serve relevant display ads, reminding them to complete a purchase or revisit your content.
9. Analytics & Metrics
Analytics inform you of campaign performance and where to optimize. Typical email metrics offer immediate insights into subscriber engagement.
9.1 Open Rates
Open Rate is often influenced by subject lines, sender names, and deliverability. Industry benchmarks vary, but a range of 15-25% is common across many sectors.
- Improve with personalization, curiosity-driven subject lines, and effective segmentation.
- Keep in Mind that Apple’s Mail Privacy Protection and similar policies can affect open rate accuracy.
9.2 Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR measures the proportion of recipients who click on at least one link in your email. A strong CTR indicates:
- Relevant Content: The offer or content resonates with the audience.
- Clear CTAs: Buttons or links are visually and contextually compelling.
Industry averages range from 2-6%, but segmented and personalized campaigns can exceed these benchmarks.
9.3 Conversion Rate
The Conversion Rate reveals how many users completed the desired action after clicking—making a purchase, signing up for a trial, or downloading a resource.
9.3.1 Return on Investment (ROI)
To calculate ROI for email marketing:
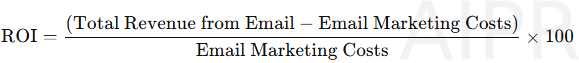
A well-executed strategy can yield an ROI of 3000% or more, making email one of the most cost-effective channels.
9.3.2 A/B Testing
A/B Testing involves sending two variations of a single email to test elements like:
- Subject Lines
- Email Layout or Template
- CTA Text or Color
Best Practices
- Test One Variable at a Time: Isolate what drives the difference in performance.
- Statistical Significance: Ensure enough subscribers are tested to yield reliable conclusions.
- Iterate Continuously: Use insights from one test to inform the next.
10. Data Security & Privacy
Respecting and protecting subscriber data isn’t just ethically correct—it’s also critical to brand reputation and regulatory compliance.
10.1 Encryption
Encryption secures data both in transit and at rest:
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): Encrypts email transmissions between mail servers.
- AES-256: Widely considered the standard for data encryption at rest.
10.2 Data Governance
Data Governance dictates how data is:
- Collected: Gaining consent or lawful basis.
- Stored: Using secure databases and backups.
- Utilized: Adhering to stated purposes in your privacy policy.
A strong governance framework prevents unauthorized access and ensures compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
10.3 Consent Management
Consent Management involves keeping accurate records of when, how, and why a subscriber opted in:
- Timestamp of Subscription
- Source (e.g., website form, event sign-up)
- Consent Terms (e.g., GDPR, marketing communications)
10.3.1 Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
SSL (now often referred to as TLS) ensures that any data input into your website forms is encrypted during transit. Pages where you collect personal information (like email addresses) should always be SSL-certified.
10.3.2 Privacy Policy
A Privacy Policy outlines:
- What Data you collect
- How You Use It
- With Whom you may share it
- Data Retention Period
Link to your privacy policy in opt-in forms and email footers to maintain transparency and trust.
11. Best Practices & Trends
Email marketing evolves rapidly. Adopting the latest best practices and trends helps keep your campaigns fresh and effective.
11.1 Mobile Optimization
With most emails now opened on mobile devices:
- Responsive Templates: Automatically adjust layout to screen size.
- Short Subject Lines: Mobile inboxes typically display fewer characters.
- Larger Buttons: Ensure CTAs are easily clickable.
11.2 Plain Text vs HTML
Plain Text Emails often feel more personal and less “promotional.” HTML Emails can showcase rich visuals and branding. Many marketers use a hybrid approach:
- HTML Layout but with minimal graphics
- Personalized Text reminiscent of a one-on-one email
11.3 AI-driven Campaigns
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming how brands craft and deliver emails. AI tools can:
- Predict Optimal Send Times
- Suggest Personalized Subject Lines
- Adapt Email Frequency based on user behavior
11.3.1 Interactive Emails
These contain elements like polls, quizzes, or sliders directly in the email. They reduce friction by allowing subscribers to interact without leaving their inbox, boosting engagement and data collection.
11.3.2 Dark Mode Adaptation
With many devices and email clients offering Dark Mode, it’s crucial to:
- Test Email Designs against different backgrounds to ensure text readability.
- Use Transparent Images or ensure images have backgrounds suited to dark themes.
12. FAQ
Below are frequently asked questions related to Business Email Lists and email marketing best practices.
- How do I grow my email list more quickly?
- Offer high-value lead magnets, use social proof in sign-up forms, and promote your newsletter or resources across multiple channels, including social media and webinars.
- Is it legal to purchase a business email list?
- While not universally illegal, purchasing lists can violate GDPR or CAN-SPAM if consent was never given. These lists often have poor engagement and higher spam risks.
- What is the difference between single opt-in and double opt-in?
- Single Opt-in: Subscribers enter their email and are instantly added to the list.
- Double Opt-in: Subscribers must confirm via a verification email. This method usually yields higher-quality subscribers and helps compliance in stricter regions.
- Why are my emails going to spam?
- Potential causes include low sender reputation, use of spam trigger words, poor engagement metrics, or missing authentication records like SPF and DKIM.
- How often should I scrub my email list?
- Ideally, every three to six months. Remove hard bounces and unengaged subscribers to maintain a high reputation.
- What are some recommended ESPs for small businesses?
- Mailchimp, Constant Contact, and AWeber are common. For e-commerce, platforms like Klaviyo or Omnisend might be more specialized.
- How many emails per week is too many?
- It depends on your audience. Start with one or two emails per week, monitor engagement and unsubscribe rates, then adjust accordingly.
- Is A/B testing complicated?
- Most modern ESPs make A/B testing straightforward. You set up two versions, pick a test segment, and the platform measures which performs better before sending to the majority.
- Should I use emojis in subject lines?
- Emojis can boost open rates if used sparingly and contextually. Overuse might trigger spam filters or appear unprofessional for certain B2B audiences.
- What metrics matter most for e-commerce brands?
- Conversion rate, average order value (AOV), and revenue per email are often more critical than just open or click rates.
- How do I handle inactive subscribers?
- Initiate a re-engagement campaign with special offers or preference updates. If they remain inactive, remove or segment them to keep your list engaged.
- Can I use chatbots or social media to collect emails?
- Absolutely. Chatbots on Facebook Messenger or direct messages on Instagram can gather leads if permission is clearly obtained, and data is stored compliantly.
- What’s the best way to track ROI across multiple channels?
- Use UTM codes on email links, Google Analytics for website tracking, and your ESP or CRM’s built-in revenue attribution tools to combine data for a holistic view.
13. Conclusion
A Business Email List remains one of the most reliable and profitable marketing assets. From building your initial list with opt-in forms and lead magnets to maintaining high deliverability through compliance and robust list hygiene, each step in the process amplifies your potential ROI. Coupled with advanced segmentation, personalization, and up-to-date best practices—like mobile-friendly design and AI-driven campaigns—you can engage subscribers more effectively than ever before.
By investing in the ongoing development of your email list and applying the strategies outlined in this guide, you position your business for sustainable growth and enduring customer relationships.



